Classification of Programming in C
0 1184
Programming in C can be classified based on levels or layers of abstraction, which helps in understanding the complexity and functionality of the code.
The main levels in C programming are Low-Level, Mid-Level, and High-Level programming.
Each level has its own set of Features, Functionalities, and Complexities.
Diagram:
Classification of Programming in C Based on Levels.
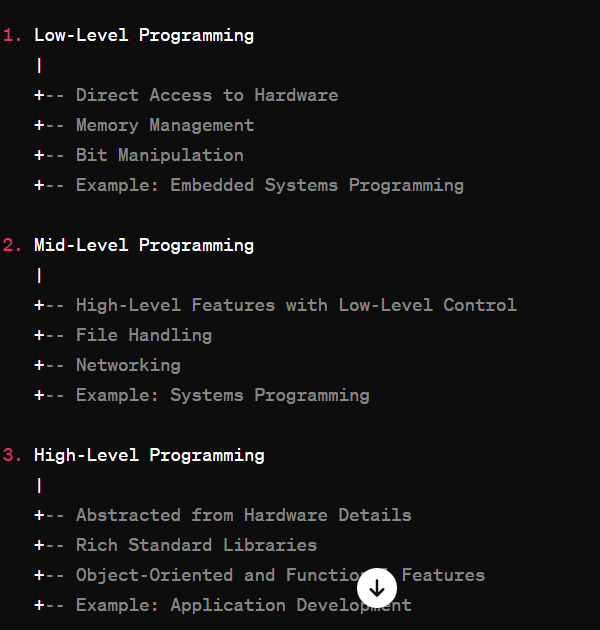
2Mid-Level Programming: High-Level Features with Low-Level Control: Combines high-level programming features with low-level control over hardware and system resources. File Handling: Provides APIs and functions to read from and write to files. Networking: Offers functionalities to create network sockets and communicate over networks. Example: Systems Programming for developing system utilities and tools.
3 High-Level Programming: Abstracted from Hardware Details: Abstracts away the hardware details, providing a more intuitive. Rich Standard Libraries: Offers rich standard libraries for common tasks like string manipulation, data structures, and mathematical computations. Object-Oriented and Functional Features: Supports object-oriented and functional programming paradigms for structured and modular code. Example: Application Development for creating desktop, web, and mobile applications.
Description of Levels in C
1Low-Level Programming: Direct Access to Hardware: Provides direct control and access to hardware components like CPU, Memory, and I/O ports. Memory Management: Requires manual memory management using pointers and memory addresses. Bit Manipulation: Involves manipulating individual bits and bytes to perform low-level operations. Example: Embedded Systems Programming for devices like microcontrollers.2Mid-Level Programming: High-Level Features with Low-Level Control: Combines high-level programming features with low-level control over hardware and system resources. File Handling: Provides APIs and functions to read from and write to files. Networking: Offers functionalities to create network sockets and communicate over networks. Example: Systems Programming for developing system utilities and tools.
3 High-Level Programming: Abstracted from Hardware Details: Abstracts away the hardware details, providing a more intuitive. Rich Standard Libraries: Offers rich standard libraries for common tasks like string manipulation, data structures, and mathematical computations. Object-Oriented and Functional Features: Supports object-oriented and functional programming paradigms for structured and modular code. Example: Application Development for creating desktop, web, and mobile applications.
Difference between Low-Level Programming, Mid-Level Programming, High-Level Programming
| Category | Description |
| Low-Level |
Closer to hardware, manual memory management, and bit-level ops.
Example: Embedded Systems Programming |
| Mid-Level |
High-level features with some control over hardware/resources.
Example: Systems Programming |
| High-Level |
Abstracted from hardware, rich standard libraries, OOP/Functional
Example: Application Development |

Share:








Comments
Waiting for your comments