River Drainage Patterns & Erosion Processes
by Devender
0 6219
There are 4 different types of Drainage Patterns that take place in any river system. River Erosion is the process that wears away the river bed and banks.
River Drainage Patterns & Erosion Processes
- River Drainage Patterns
- Most of the rivers of the Indo-Gangetic Plains are of dendritic type
- This drainage pattern is found in the Vindhyan Mountains of India
- The old folded mountains of the Singhbhum (Chotanagpur Plateau) have drainage of trellis pattern
- A good example of a radial drainage pattern is provided by the rivers originating from the Amarkantak Mountain
- Rivers like Narmada, Son, and Mahanadi originating from Amarkantak Hills flow in different directions and are good examples of the radial pattern
- Processes of river action
- Materials in Solution - minerals that are dissolved in water
- Materials in Suspension - Suspension of Sand, Silt & Mud in water
- The Traction Load - Coarser materials such as pebbles, stones, rocks & Boulders
- River Erosion & Transportation Processes
- Lateral corrasion is sideways erosion that widens the V-shaped valley
- Vertical corrasion is the downward action that deepens the river channel
There are 4 types of drainage patterns that exist in any river system namely:
1 Dendritic Drainage Pattern
If the rocks are composed of homogeneous beds of uniform resistance to erosion, the tributaries will join the mainstream obliquely as insequent streams. The drainage pattern so formed will be in a tree-like appearance. So, it is termed Dendritic drainage.
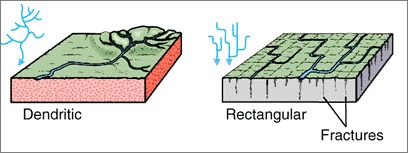
2 Rectangular Drainage Pattern
It is found in regions that have undergone faulting. It develops on rocks that are of approximately uniform resistance to erosion, but which have two directions of jointing at approximately right angles.
These joints are usually less resistant to erosion than the bulk rock so erosion tends to open the joints and streams eventually develop along the joints. As a result, a stream system in which streams consist mainly of straight line segments with right-angle bends and tributaries join larger streams at right angles.
3 Trellis Drainage Pattern
It develops in folded topography like the ones found in the Appalachian Mountains of North America. The rocks are made up of alternate layers of hard & soft rocks, hence tributaries tend to follow the pattern of rock structure.
This pattern occurs when tributaries join the mainstream and erode a valley at approximately right angles in a pattern that resembles a garden trellis.
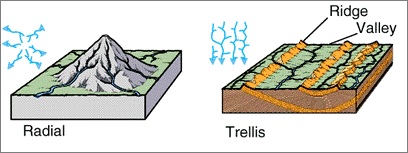
4 Radial Drainage Pattern
This pattern is characterized by outflowing rivers, away from a central point, analogous with the spokes of a wheel. It tends to develop on the flanks of a dome or a volcanic cone.
This pattern can also be found in the Girnar Hills (Kathiawar, Gujarat), and the Mikir Hills of Assam.
When a river flows, it carries eroded materials with it. These materials can be divided into 3 types:
The volume of the water, the velocity of the flow & size, shape, and weight of the load decide the ability of the river to move the various grades of materials. Transporting power of a river can be increased by more than 10 times by just doubling its velocity.
1 Corrasion/Abrasion
Mechanical grinding of river's traction load against the banks & bed of the river. The rock fragments hurdle against the sides as well as the bottom of the river leading to lateral & vertical corrasion.
2 Corrosion/Solution
The chemical action of water on soluble or partly soluble rocks with which rivers come into contact.
For Example - in the case of Calcium carbonate.
3 Hydraulic Action
The mechanical loosening & sweeping away of materials by river water mainly by surging into the crevices & cracks of rocks & disintegrating them.
4 Attrition
The wear & tear of transported material among them when they roll and collide into one another.

Share:







Comments
Waiting for your comments