Types of coasts
by Devender
0 4452
There are many kinds of coasts but they can be divided into two categories on the basis of coastline that are - Coastline of Submergence and Coastline of Emergence.
Types of coasts
- Coastline of Submergence
- The drowning of river valleys along a stretch of coast and the formation of rias results in an extremely irregular and indented coastline
- A ria coast differ from the fiords in two ways that are - they are not glaciated, & their depth increases seaward
- The fjord is formed when a glacier retreats, after carving its typical U-shaped valley with the sea filling the resulting valley floor
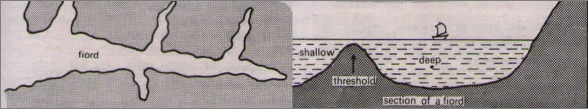
- It forms a narrow, steep-sided inlet connected to the sea
- The terminal moraine pushed down the valley by the glacier is left underwater at the fjord’s entrance
- It causes the water at the neck or mouth of the fjord to be shallower than the main body of the fjord behind it
- Therefore, the opening toward the sea is often shallow & termed as a threshold
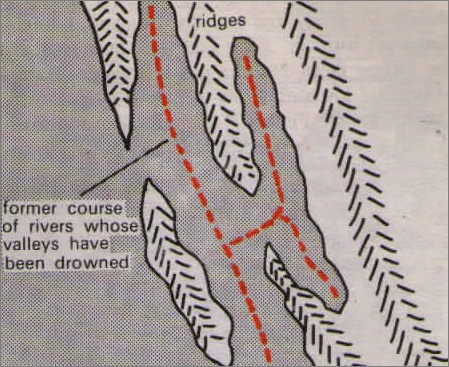
- The elongated islands are the crests of former ranges & the narrow inlets were the former longitudinal valleys
- Like ria and fiord coasts, the mountainous nature of the Dalmatian coastline hinders inland communication
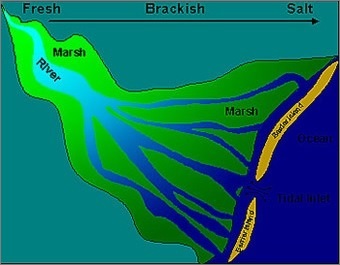
- Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environments
- They are subject both to marine influences such as tides, waves, and the influx of saline water
- They are subject to riverine influences such as flows of fresh water and sediment
- Coastlines of Emergence
- Where the emerging deposits from the continental shelf are sandy & gravelly, beaches & marine dunes are formed
- Ports that were once located on the former coast, became inland towns
- This coast is quite straight with steep cliffs & deeper offshore waters
These are formed by the sinking of the land or the rise of the sea. It includes coasts such as - Ria coasts, Fjord coasts, Estuarine coasts & Dalmatian/Longitudinal coasts.
1 Ria Coasts – Drowned river valleys
During the ice age, a great amount of water was locked up in the ice. When the climate got warmer, the ice got melted, and hence, the sea level increase.
In the upland coastal regions, where the mountain runs at a right angle to the sea which is transverse to the coast, a rise in the sea level submerges or drowns the lower parts of the valleys to form long narrow branching inlets separated by narrow headlands. Therefore, a coastal inlet formed by the partial submergence of an unglaciated river valley that remains open to the sea & is a coastline having several parallel rias separated by prominent ridges, extending a distance inland.
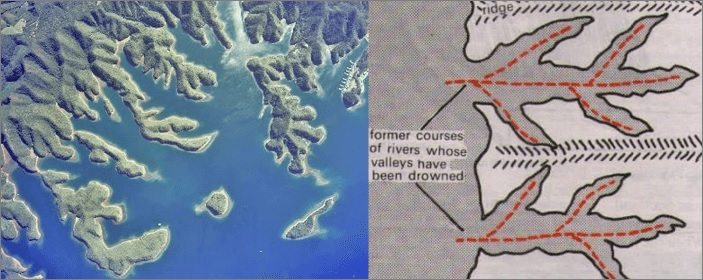
All rias are extensively used for sitting fishing ports & naval bases and are backed by highlands & support few large commercial ports.
2 Fjord coasts – Drowned glaciated valleys
Fjords were created by glaciers that moved very slowly over time, and greatly altered the landscape once they have moved through an area carving deep valley and the process is known as glaciation.

3 Dalmatian coasts
It is a longitudinal coast where the mountains run parallel to the coast. The submergence of the coastline produces long, narrow inlets with a chain of islands parallel to the coast.
4 Estuarine Coasts
These are the coasts made by estuaries, with streams of river freely flowing into the sea, making them excellent sites for the ports. An estuary is a partly enclosed coastal body of brackish water (salinity between saline seawater & fresh river water) with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea.
These are formed due to the uplift of the land or fall in the sea level. These are less common & include uplifted lowland coast & emergent upland coast.
1 Uplifted lowland coasts
The uplifted part of the continental self produces a gently sloping coastal lowland. The offshore waters are shallow with the lagoons, salt marshes & mudflats.
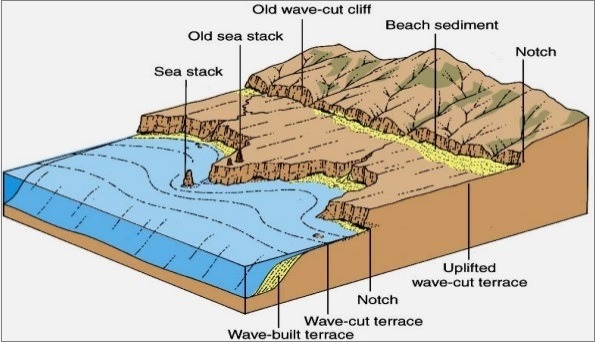
2 Emergent upland coasts
Coastal plateaus thurst up by faulting & earth movements that the whole region is raised forming a raised beach. A raised beach is beyond the range of waves, though it may still possess arches, stacks & other coastal features.

Share:







Comments
Waiting for your comments