HTML Elements
0 6387
Elements are the building block of an HTML code. Let's take an example of the previous tutorial in which we have used several elements for defining body, headings and paragraphs, etc. Take a closer look at the tag given below.
<p>
It consists of a Left-Angle Bracket (<), a character (p), and a Right-Angle Bracket(>). This is a starting tag and character between indicates the purpose of the tag. In the above example, the character "p" is for a paragraph.
Tags generally come in pairs with few exceptions (which we will learn in subsequent chapters). Now let's look at the another part which is a closing tag for the paragraph.
</p>
It also consists of a Left-Angle Bracket (<), a forward slash (/), a character (p), and a Right-Angle Bracket (>). The forward-slash (/) here makes it different and suggest that it is a closing tag for the paragraph.
Together with opening tag (<p>) and closing tag (</p>) along with the content in between the makes an element.
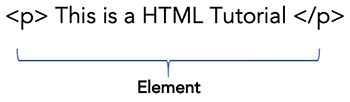
Element
Term Elements and Tags are often interchanged, but technically speaking, the element is made up of opening tag, closing tag along with the content between them.
Some other common tags which come in pair are:
<h1>: Used for headings
<h2>: Used for subheadings.
<b>: Used to make content bold.
<i>: For italics.
Examples of tags which don't come in pairs:
<br/>: Used for a line break.
<hr/>: This is for a horizontal break.
The element which have only single tag are called empty elements (see: elements are tags are often interchanged).
These empty elements don't have any content in between them. The tag for these types of elements have a forward slash and space before the closing angled bracket.
See you in the next chapter

Share:








Comments
Waiting for your comments