Lord Dalhousie
by Devender
0 3115
Lord Dalhousie held the post from 1848 to 1856 and he gave a lot of things to India that is why he is known as the father of many things in India.
Lord Dalhousie
He was the youngest Governor-General of India at the age of 36 years. He shifted the headquarters of Bengal Artillery from Calcutta to Meerut and made Simla the permanent headquarters of the army & summer capital. The formation of Gurkha regiments also took place during his reign.
He is also known as:
- Father of Indian Telegraph
- Father of Indian Railways
- Father of Indian Postal system
- Father of Indian Engineering Services
- Maker of modern India
- The doctrine of Lapse:
- Reforms and Developments:
- Woods Dispatch:
- It asked the government to take responsibility for educating the masses
- It was eliminating the downward filtration theory at least on paper
- It systemized the hierarchy from vernacular primary schools in villages at the bottom
- Above the schools were Anglo-Vernacular High Schools and after that an affiliated college at the district level and affiliating universities in the presidency towns of Calcutta, Bombay, and Madras
- It recommended the use of the local language at the school level and English for higher studies
- It also pointed towards the improvement of female and vocational education and teachers training
- Charter Act of 1853:
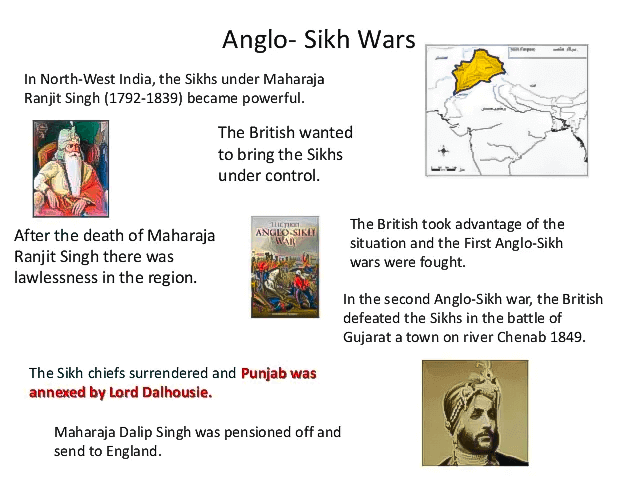
He followed the policy of annexation and annexed Burma with the second Burmese war and annexed Awadh. He also annexed Punjab after the Second Anglo-Sikh war. He founded the Doctrine of Lapse for further annexation of Indian Empires.
This was a policy that was based on differences in principle b/w right to inherit property & right to govern. It restricted the alliance kings to adopt an heir if they didn't have a son to the heir to their kingdom.
It helped Britishers to lapse Satara, Jaitpur and Sambhalpur, Udaipur, Nagpur, Jhansi, & Awadh in the given order. The annexed states were monitored by chief commissioners with the introduction of centralized control called a non-regulation system for modern centralized states.
1 Telegraph:
4000 miles of lines were laid down under the supervision of O’Shaughnessy in 1852 which connected Calcutta, Peshawar, Bombay & Madras telegraphically. It provided a great advantage to Britishers during the revolt of 1857.
2 Railway:
Dalhousie started the Guarantee system which guaranteed a minimum interest of five percent to railway companies on their investment. The government retained the right to buy the railway and the railway was mainly used for Defence, Commercial & Administrative reasons.
The first railway line was from Bombay to Thane in 1853 and the second one was from Calcutta to Raniganj coal fields in 1854. The third line was from Madras to Arakkonam in 1856.
3 Postal System:
Dalhousie laid down the foundation of the modern postal system in 1854 with the introduction of postal stamps although, the Postal system existed from 1837.
4 IES:
He created separate public work departments and allotted a lot of funds for cutting canals and roads. In 1854, the upper Gangetic panel was cut and many bridges were constructed.
5 Social & Educational
He passed the Widow remarriage act in 1856 and recommended the setting up of universities in Calcutta, Bombay, and Madras. During his time in 1853, competitive examination for the Indian Civil Services began and written exams started in 1854 in India.
Educational changes of Sir Charles wood (1854) are viewed as scholarly diagrammed of India which gave a layout to Primary, Secondary, and Collegiate degrees of schooling.
Charles Wood created a dispatch on an educational system for India in 1854 which was considered as the "Magna Carta of English Education in India". It was the first comprehensive plan to spread education in India.
It stated that the education imparted in government institutions should be secular. It also recommended a system of grants-in-aid to encourage private enterprise.
It further added 6 members to the Gov. General council making it a body for legislative purposes. These six members were: Chief Justice of India, Sitting Judge of Supreme court, and 4 representatives of NWFP, Bombay, Madras, and Bengal.
It made Indian civil services an open competition and Macalay was made chairman of the Indian civil services committee.

Share:







Comments
Waiting for your comments