Government of India Act, Indian Councils Act, Lord Lytton
by Devender
0 2528
After the revolt of 1857, Britishers were forced to make a lot of changes like the Government of India Act and the Indian Councils Act.
Government of India Act
It came out in 1858 and under this act, the administration of India was transferred to the British crown instead of the East India company.
- The title of General was made Viceroy
- Lord Canning became the first Viceroy of India
- Acc. to it, the viceroy was to be assisted by an executive council whose members were to act as the heads of various departments
- The Secretary of State for India would be a member of the British cabinet
- Indian Council consisted of 15 members to assist Secretary
- Charles Wood became the first Secretary of State for India
- Queens Victoria’s proclamation:
- Finally, the inclusion of Indians in the Legislative Council took place
- However, the functions of these members were strictly limited to making legislation that was subjected to the approval of the Viceroy
- They were not allowed to interfere in Executive Council's matters
- They didn't possess any powers of administration and finance
- Lord Mayo:
- He was known for opening Rajkot College in Kathiawar
- He also opened the Mayo College at Ajmer for political training of Indian princes
- He also established the Statistical Survey of India and the Department of Agriculture and Commerce
- He introduced the state railway
- Lord Northbrook:
- Royal Titles Act:
- 1877 for Queen Victoria
- 1903 for Edward 7 and Alexandra
- 1911 for George 5 & Mary
- First Famine Commission:
- Vernacular Press Act:
- Second Anglo-Afghan War:
- Arms Act of 1878:
- Uniform salt tax:
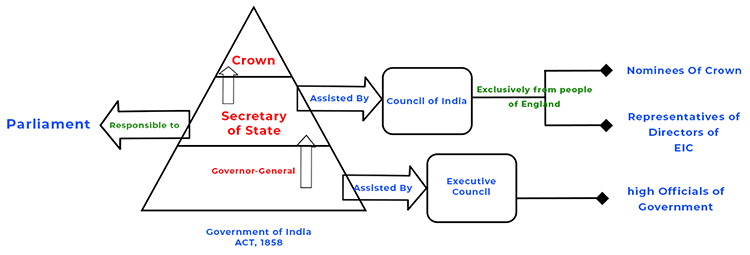
Court of Directors and Board of Control were ended in England and Secretary of State for India and India Council were made in its place.
All the decisive powers remained with the secretary and all other members were just for advisory purposes hence, the dual system introduced by Pitt’s India Act of 1784 came to an end.
It is also known as the Magna Carta of the Indian people. Lord Canning formed the new government at Allahabad in November 1858 according to the proclamation of Queen Victoria.
They agreed to not look for any further expansion of territory and promised to be tolerant towards every religion. They also endorsed the treaty made by the Company with the Indian prince and promised to respect their rights, dignity, and honor. Queen pledged to provide equal treatment of all her subjects and Equal & impartial protection of the law.
Indian Councils Act
It came out in 1861 and acc. to it, a fifth member was added to the viceroy’s executive council. The Governor-General’s Executive Council was enlarged into a Central Legislative Council and 6 to 12 additional members were to be nominated by the Governor-General. This act provided that not less than half of these members were to be non-officials/Indian members.
Legislative Councils were established in the provinces also. The number of additional members in the provinces was fixed from 4 to 8. This act let Indian people be involved in the law-making process.
He held the office from 1869 to 1872. He was killed by a convict, Sher Ali who stabbed him to death at Port Blair in 1872. He held the first census in Indian history in 1871.
He held the office from 1872 to 1876 and during his reign, the deposition of Gaekwad in 1874 took place. It was during his time period that Prince of Wales visited India, the famous Kuka movement took place, and famine in Bihar and Bengal in 1873-1874 took place.
Lord Lytton
He held the office from 1876 to 1880. He laid the foundation of Mohammedan Anglo-Oriental College at Aligarh in 1877. During his time, a famine that was the result of the failure of two monsoons from 1876 to 1878 took place. Cholera and fever outbreaks also put salt on the wounds of Indian people.
Happened in 1877, Queen Victoria assumed the title of Kaiser-i-Hind or Queen Empress of India at Delhi Darbar. The Delhi Darbar which was also known as Imperial Darbar was held three times by Britishers:
He appointed the First Famine Commission under Sir Richard Strachey. It suggested for provision of funds for famine relief and construction work in the annual budget.
It came out in 1878 which crushed the freedom of the Indian press. It basically empowered Magistrate to take an undertaking from local news agencies editor, publisher, and printer to not print anything against the English government and if done so, their equipment will be seized.
Britishers emerged victorious in this war and the Treaty of Gandamak was signed. Afghan policy of British residents at Kabul was aimed to stop the expansion of the Russian Empire into India.
It prevented Indians to keep arms without a license. However, it didn't include Anglo Indians or Europeans.
He introduced the uniform salt tax in India which abolished many trade import duties. It adversely affected Indian Industries & its economy.

Share:







Comments
Waiting for your comments