Lord Cornwallis, Richard Colley Wellesley, Subsidiary Alliance
by Devender
0 1640
Lord Cornwallis was a British army officer, civil administrator, and diplomat whereas Richard Colley Wellesley gave the Subsidiary Alliance.
Lord Cornwallis
He held power from 1786 to 1793 and made amendments in the Pitts Act taking extraordinary Legal Powers to overrule the decision of the Council of Ministers. He founded the Zamindari system/Permanent settlement of Bengal according to which Zamindari was greater than Mahalwari which was greater than Ryotwari.
It was also known as the Decennial settlement because farms were given to Zamindars for 10 years. The revenue was fixed and was not liable to change where 10/11 went to the company and the remaining 1/11 went to Zamindar. It was mainly used in Bengal, Bihar, and Banaras.
- He is known as the father of Indian Administrative Services
- He used to make appointments on the basis of merit in civil services but he made civil services only for Europeans
- All high Indian officials were dismissed and made reservations of these posts for only Europeans
- He also established a regular police force & established thanas in the district under Darogas with the head of thanas as SP
- He provided separation of powers between Commercial, Judicial & Revenue officials
- He made 4 provincial courts at Calcutta, Dhaka, Patna & Mursiddabad along with District courts
- Cornwallis created a European state within the framework of Indian traditions
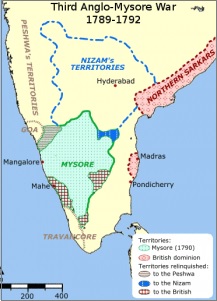
- Third Anglo-Mysore War:
- The Raja of Coorg got independence from Tipu
- Tipu Sultan had to provide 3 Crore rupees and 2 of his sons to Cornwallis as hostages to ensure 3 Crores are paid in regular installments
- He followed the policy of non-intervention with other states and territories
- It resulted in the Nizam employing French officers to train his army thus decreasing the English influence
- Marathas and Tipu Sultan also did the same undermining Britishers
- He remained in power till 1798
- Subsidiary Alliance:
- Any alliance will have to maintain a contingent of British troops in his territory commanded by British officers
- Another important point of it was that Indian states had to cut their connections with any external powers like the French
- Indian states were also forbidden to make any political connections with any other state even Indian without British permission
- States were also asked to disband their armies and keep a British resident at their court forbidding them to employ any other Europeans in their court/service without British permission
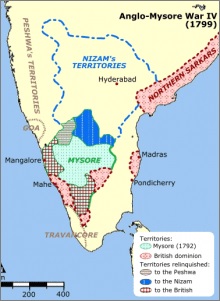
- Fourth Anglo Mysore war:
- Tipu Sultan:
- Second Anglo Maratha War:
- In 1803, the second Anglo-Maratha war broke out in Central India
- Britishers were able to win and Richard Colley Wellesley undertook Maratha Empire by Treaty of Bassein & Treaty of Deogaon
- He made East India company from a trading company to imperial power in India
- Sir George Barlow (1805 – 1807):
- Lord Minto 1 (1807 -1813):
- It allowed Christian missionaries to come to India and preach Christianity & modern education leading to Social reforms in India
- It also ended the monopoly in the Indian Commercial market except for tea & trade with China
- Now, other British companies can also trade in India.
In 1791, The Sanskrit College was established by Jonathan Duncan at Benaras for the study of Hindu law and philosophy
It happened between Lord Cornwallis and Tipu Sultan where Marathas and Nizam were on Britisher's side. As a result, Tipu Sultan was defeated and Treaty of Rangpatnam according to which, half of Tipu's territories were taken from him and distributed among Marathas, Nizam, and Britishers.
Sir John Shore
He was the principal revenue adviser during the regime of Warren Hastings, the first Governor-General of India. He was the man behind most of the reforms in the revenue administration in 1786 and 1790.
The Court of Directors was so impressed by Shore’s reasoning and knowledge and his genuine concern for the interests of the company and the people, that he was appointed the Governor-General of India in 1793.
Richard Colley Wellesley
He used to call himself "Bengal Tiger". He reversed the policy of the Non-intervention of John Shore and opened the Fort William College at Calcutta to train the Company’s servants in Indian languages & customs. However, it was closed soon in 1802. He was the one who gave the Subsidiary Alliance with an aim to remove the French and establish British Power.
According to it, Indian states will be known as protected states whereas the British will be the paramount power. Britishers will save Indian states from external aggression or Invasion in exchange for money or part of the territory to support the subsidiary troops.
According to this alliance, the Britishers will not interfere in any internal affairs of protected states. The First alliance was made by Nizam of Hyderabad.
It was fought between Tipu Sultan and Britishers where Britishers were supported by the Nizam. Tipu was killed in the battle and all his territory was divided among British and Nizam. They crowned a five-year-old boy named "Krishanraja 3" making Mysore a princely state under East India Company.
He partnered with Turkey, French, Arabia & Kabul and set up his embassies there. He also started a Jacobian club at Srirangpatnam with the plantation of the tree of liberty. He received a letter of friendship from Napolean Bonaparte. He used to say "Better to live like a lion for a day than a lifetime as a sheep". He used the iron-cased rockets in the Third and Fourth Mysore war and wrote Fathul Mujahidin.
This war happened because of the defeat of the Peshwa Baji Rao II by the Holkars, one of the prominent Maratha clans. As a result of this defeat, Peshwa accepted British protection by signing the Treaty of Bassein in December 1802.
The other Marathas like the Gwalior’s Scindia rulers and the Bhonsle rulers of Nagpur and Berar did not accept this and they wanted to fight against the British.
He converted British Empire in India to the British Empire of India.
He was famous for the Mutiny of Vellore in 1806 in which the Indian soldiers killed many English officials.
He signed a treaty with the Shah of Persia and another treaty known as the treaty of Amritsar with Raja Ranjit Singh. Charter act (1813) was passed during his period.
Charter Act
The Regulating act of 1793 made it compulsory to renew the charter act every 20 years which was passed by the government in 1793. The Charter Act provided 1 Lakh yearly for advancing information on modern sciences in the country.
In any case, even this unimportant sum was not made accessible till 1823, essentially in light of the debate seethed on the topic of the bearing that this consumption should take.

Share:







Comments
Waiting for your comments