India Physiography – Indian Desert, Coastal regions, Indian Islands
by Devender
0 1584
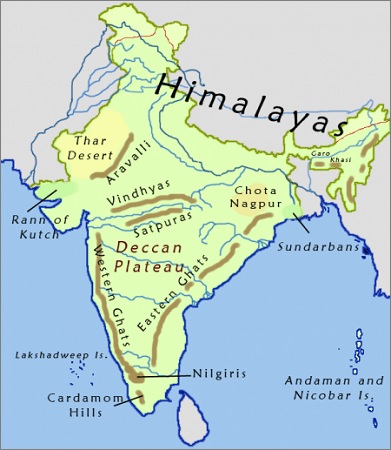
India can be divided into 6 physical divisions which are:
- The Northern Mountains
- The North Indian Plain
- The Peninsular Plateau
- Great Indian Desert
- The coastal Regions
- Islands
- Western Coastal Plains
- Eastern Coastal Plains
- Kathiawar Coast - Kutch to Daman (Tapti, Narmada, Sabarmati & Mahi river deposit a huge load of sediments in the Gulf of Cambay & form estuaries)
- Konkan Coast - Between Daman & Goa
- Kanyakumari Coast - Between Cannanore & Cape Camorin
- Malabar Coast - Kannada + Kanyakumari Coast
- Mumbai
- Marmagoa
- Cochin
- Mangalore
- Nhava-Sheva
- Kandla
- Ashtamudi
- Vembanad called Kayals
- Utkal Coast - Deltaic plains of Ganga to Mahanadi delta (Famous Chilka lake is located in this plain)
- Andhra Coast - Utkal plains to Pulicat lake (Contains deltas of Godavari & Krishna Rivers, & famous Kolleru lake)
- Northern Circars - Utkal Coast + Andhra Coast (Between Mahanadi & Krishna)
- Coromandal Coast - Between Krishna & Kanyakumari (Consist of Kaveri Delta)
- Chilka Lake (Orissa) - It is the largest saltwater lake in India and lies in the state of Odisha, south of the Mahanadi Delta
- Pulicat (Tamilnadu)
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal consist of hard volcanic rocks
- The middle Andaman and Nicobar Islands are the largest islands in India
- The Lakshadweep islands in the Arabian Sea are formed by corals
- Andaman & Nicobar Islands:
- These islands are formed of Granite rocks
- These islands have high hills
- The climate is equatorial with tropical rain-forests
- Lakshadweep Islands:
- These islands have calcium-rich soils filled with organic limestone
- These islands also have scattered vegetation of palm species
- A & N Islands - Continuation of Arakan Yoma mountain range of Myanmar
- Nicobar - Just 147 km from Sumatra island (Indonesia)
- Saddle Peak - Highest Peak of Andaman
- Pamban Island - Between India & Srilanka
- Salasette - Group of 7 islands, known as Mumbai today
- Diu - Fishing Island
- New Moore Island - Disputed site b/w India & Bangladesh
- Wheeler Island - Missile launching island in BOB (Near Odisha coast)
- Sriharikota - Split Island (Rocket launching site in BOB in Andhra Pradesh)
- Wellington - Naval Station (Kerala)
- Strategic significance - India overlooks some of the most important sea lanes such as the Suez Canal, Malacca Strait
- Economic significance - It is a 2.02 million sq km Exclusive economic zone with a long coastline
- Tourism significance - Marine biodiversity and rich ecosystem with coral reefs, mangroves
- It has large fishing potential
- Wave energy & Tidal energy potential
- It is a zone of Hydrocarbons
- Generation of Southwest Monsoon
The Great Indian Desert
The great Indian desert extends from the western margins of the Aravali Hills and has only one prominent river that is Luni.
The Coastal regions
The mainland of India has a length of 6,100 km of coastline excluding the Islands. It extends from the Gangetic delta in the east to the Kutch of Gujarat in the west.
The coast of India is divided into two parts:
The coastal regions of India are very well known for providing important hinterlands for the ports and also for agriculture, trade, industrial centers, tourist centers, fishing, and salt making.
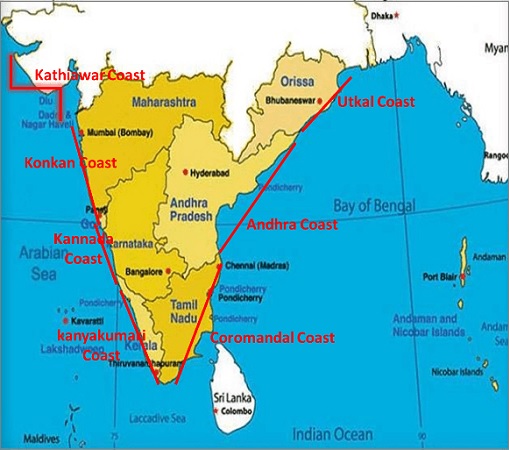
1 Western Coastal Plains:
The Western coastal plains lie between the Western Ghats & the Arabian sea from Gujrat in the north to Kanyakumari in the south. These are narrow & wet as compared to Eastern Coast. It is further divided in:
Its Important Ports are:
Marked with Lagoons:
2 Eastern Coastal Plains:
These lie between the Eastern Ghats & the Bay of Bengal from the Gangetic delta in the north to Kanyakumari in the south and are known as the Land of Deltas such as Mahanadi, Krishna, Kaveri & Godavari.
The Eastern coastal plains are broader but drier as compared to Western plains. It is further divided into sub coasts namely:
There is also a freshwater Kolleru Lake that lies between Godavari & Krishna rivers.
Lagoons:
Indian Islands
There is a total of 247 islands in India out of which 204 islands are in the Bay of Bengal and the remaining 43 in the Arabian sea. There are a few coral islands in the Gulf of Mannar also.
The Southernmost point of India is in Nicobar Island and it is known as Indira Point. It was formerly known as Pigmalion Point. After the 2004 Tsunami, it got submerged underwater and it is still submerged.
These are Volcanic islands representing submarine volcanism. These also represent the surfaces of submerged folds namely extension of Himalaya, precisely Arakan Yoma fold mountains of Myanmar.
These islands are a union of coral islands and comprise a large number of dead corals, fringing, barrier, and atoll coral reefs.
Prominent Indian Islands:
Significance of the Indian Ocean for India:

Share:







Comments
Waiting for your comments