Atmosphere – Evaporation, Humidity, Condensation, Precipitation
by Devender
0 2314
Atmosphere – Evaporation, Humidity, Condensation, Precipitation
- Evaporation:
- Evaporation increases with temperature, dryness, and movement of air
- It decreases with cloud cover
- 64% by Transpiration
- 6% by Soil Evaporation
- 3% from water bodies
- Humidity:
- Humidity increases with an increase in temperature
- At any given temperature, the air can hold a definite limit of water vapor which is known as saturation point
- The air at the saturation point is known as the saturated air
- The temperature at which saturation occurs is called the Dew point
- Absolute Humidity:
- Specific Humidity:
- Relative Humidity:
- Condensation:
- When water vapors directly convert to solid form, is called sublimation
- Condensation happens in free air from cooling around very small particles which are known as condensation nuclei
- When air is reduced to dew point with its volume remaining constant
- When temperature and volume of air are both reduced
- When moisture is added to the air through evaporation
- Form of Condensation:
- It forms when moisture is deposited in form of water droplets on cooler surfaces of solid objects instead of nuclei in the air above
- It forms when the temperature of the air falls below the dew point but stays above the freezing point
- It forms on solid surfaces when condensation takes place below the freezing point
- It means the dew point is at or below freezing point
- Fog is formed when cold and warm currents meet
- Mist is frequently formed over mountains when rising warm air up the slopes meet cold surfaces
- The difference between Fog and mist is that mist contains more moisture than fog and each nuclei in mist contains a thicker layer of moisture
- In industrial and urban areas, smoke provides enough nuclei for the formation of fog and mist
- When smoke is mixed with fog, it is called smog
- Clouds:
- Cirrus Clouds
- Cumulus Clouds
- Nimbus Clouds
- Stratus Clouds
- Precipitation:
- Snowfall
- Sleet
- Hail
- Rainfall
- Types of Rainfall:
- Heavy rainfall takes place along with thunder and lighting but doesn't last long
- It is common in Equatorial & Tropical regions in summers daily
- When these winds cross the mountain range & descend along its leeward side
- It gets dry and warm causing only a little rain
- It can occur in any season
- At the warm front, the warm wind rises over the cold air
- As the warm air rises, it becomes cold and condenses to form clouds altostratus clouds
- This rain carries on for hours to days
Evaporation is the process by which water or a liquid is transferred from a liquid state to a gaseous state.
The evaporation of water happens from different sources in the atmosphere:
Humidity is defined as the amount of water vapor present in the air.
It is measure in gm/m3 and is the weight of the actual amount of water vapor present in a unit volume of air.
It is measured in gm/kg and is the weight of water vapor present per unit weight of air. It is not affected by changes in pressure or temperature.
It is expressed in percentage and is the ratio of water vapor in air at a particular temperature to the total amount of water vapor required to saturate the same air at the same temperature.
It increases with the increase of water vapor in the air and it decreases with an increase in temperature. It is measured with Hygrometer.
It is defined as the transformation of water vapor into the water due to the loss of heat when moist air gets cooled. The cooling reaches the level where air's capacity to hold water vapor ceases and then, excess water vapors condense into liquid form.
The particles of dust, smoke, and salt from oceans are considered good nuclei as they have the tendency to absorb water. Condensation takes place in the following cases:-
Dew
Frost
Fog and Mist
Smog
Clouds are a mass of minute water droplets or tiny crystals of ice formed by condensation of water vapor in free air which are formed mainly because of adiabatic cooling of air below its dew point.
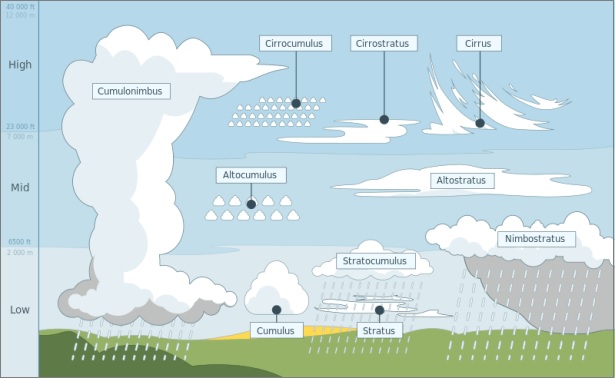
These are formed at high altitudes around 8-12 km above the surface and are thin, white in colour, composed of ice crystals, and have a feathery appearance.
These exist in patches and are formed at 4-7 km above the surface. These look like cotton wool and have a flat base.
These forms near the earth's surface and are extremely dense. These are opaque to sun rays. The color of these clouds is black and grey.
These clouds forms due to loss of heat or mixing of air masses at different temperatures. These clouds cover almost all of the sky and occur in form of sheets of layers.
The condensation of water vapor in the air in the form of water or ice falls on the earth's surface, it is known as precipitation.
It happens when condensation takes place below the freezing point which means water vapor is directly converted into a solid-state. The precipitation occurs in the form of snowflakes.
When a layer of temp. above freezing point overlies a subfreezing layer near the ground, precipitation occurs in form of sleet. It is a frozen raindrop or refroze melted snow water.
Sometimes, the raindrops get solidified after leaving the clouds into small round-shaped stones pieces of ice which are known as hailstones. These are formed when raindrops pass through colder layers and become solid. These contain several concentric layers of ice, one over the other.
It is the most common type of precipitation. It occurs in the form of water and is known as cloud particles.
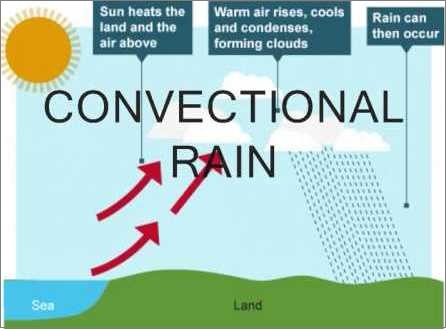
Convectional Rainfall:-
When the air gets heated it becomes light and rises up as convectional currents. As it rises up, it loses heat and condensation takes place with the formation of cumulus clouds.
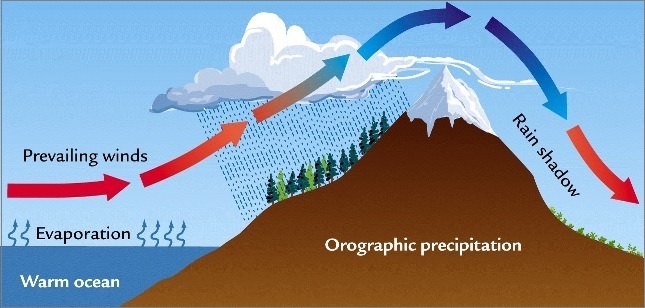
Orographic/Relief Rainfall:-
When a warm and moist air current is obstructed by a mountain range, it is forced to ascend along its slopes. This ascending causes cooling of the air current and its temperature falls down below dew point causing rainfall on the windward slope of the mountain range.
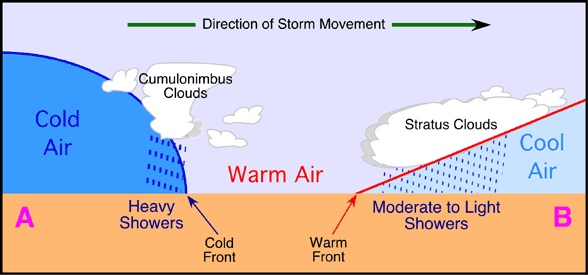
Cyclonic/Frontal Rainfall:-
The rainfall which is associated with cyclones is known as Cyclonic/Frontal Rainfall. It occurs along the fronts of the cyclone.

Share:







Comments
Waiting for your comments