Formation of Continents – Continental Drift Theory & Plate Tectonics
by Devender
0 1900
Formation of Continents – Continental Drift Theory & Plate Tectonics
- Wegner's Continental Drift Theory:
- Matching Coastlines of continents across water bodies – The Africa and South America continents are almost a perfect fit at 1000 fathom line
- The similarity of Age of the rocks across different continents on the edges of the jigsaw fit
- Similar Fossil evidence of organisms (plants & animals) across jigsaw fit borderlines
- Palaeo-climatic evidence Glacial evidenced in Tropical lands
- Ghana have rich placer deposits of gold in spite of having no source rock there but in Brazil
- Some parts of Pangea moved westward while some moved equatorward
- The sediments deposit in the Tethis sea suffered folding, resulted in the formation of the Himalayas & Alps
- Westward drift resulted in wrinkling edges of America & Rockies and Andes were formed
- Plate Tectonics:
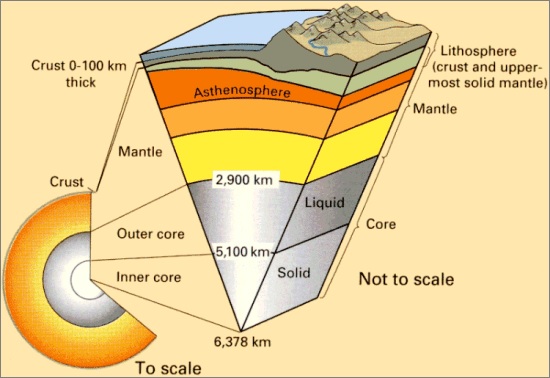
- Crust and upper Brittle part of mantle together form the lithosphere
- The crust is made up of Continental Crust (40-60 km) and Oceanic crust (1-2 km)
- Asthenosphere has unique mechanical rigidity, semi-molten, plastic
- Lithosphere float over Asthenosphere
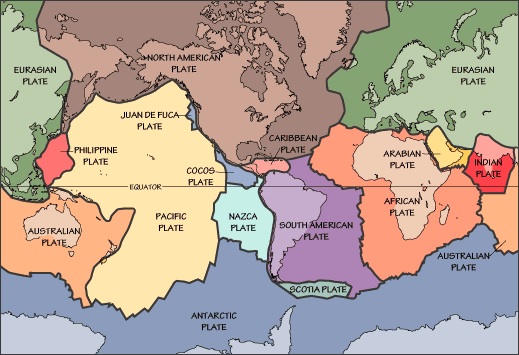
- The lithosphere is broken into plates
- Earth Plates:
- Plate Interactions:
- Divergent Boundary
- Convergent Boundary
- Transverse Boundary
- High-density plate will subduct
- High-Velocity plate will subduct
- High mass & area plate will subduct
- Divergent boundaries:
- Convergent boundaries:
- Transverse boundaries:
In 1912, Alfred Wegner proposed his theory of Continental Drift which is also known as the Jigsaw Fit Theory. It was the first one to propound the movement of continents. He made the following observations in his theory:
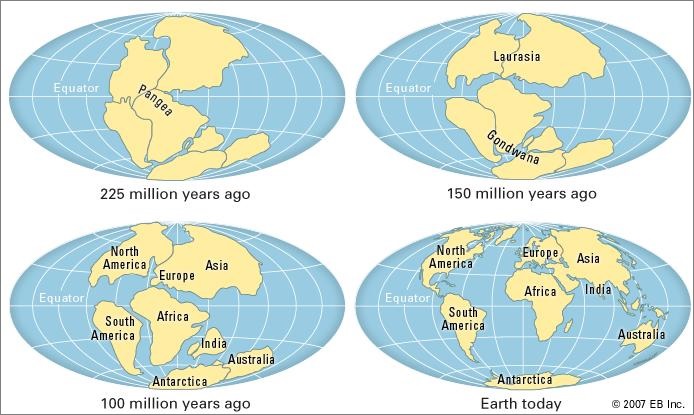
According to Wegner, all the continents were once a single landmass known as PANGAEA and there was a mega ocean called PANTHALASSA.
Around 200 million years ago, the PANGAEA started to split into 2 large landmasses known as Laurasia and Gondwanaland which further broke down into many smaller continents.
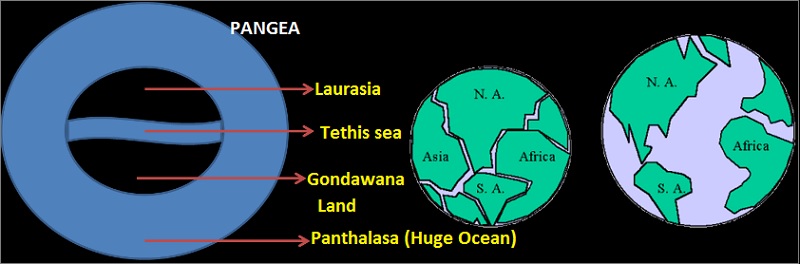
Although most of the points of the Wegner theory were rejected, the central idea of the horizontal movement was kept and evidence from this theory became the base for modern theories like Plate Tectonics theory.
It is considered the most latest and it is also the most accepted theory. It states:
There are 7 major plates on eath namely:
1 Pacific Plate
2 North American Plate
3 Eurasian
4 African Plate
5 Antarctic Plate
6 Australian Plate
7 Australian Plate
The rigid lithospheric plates move independently in different directions over the Asthenosphere.
Subduction of plates
The plates moving away from each other. The different phases of this are:
Rift valley formation that leads to Nascent Sea Formation and finally, Ocean formation.
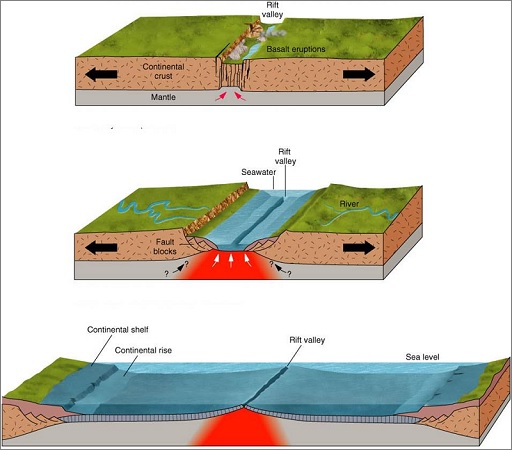
For example - The Great African rift valley + Red sea – Nascent sea
The plates come towards each other and collide leading to the formation of volcanic mountains and folded mountains.
For example - Andes, Rockies, Atlas mountain (Africa)
Part of these plates are melted forming magma. This magma rises to the surface which forms volcanic mountains or Trench.
These plates can not fold under each other and hence, mountains are formed.
Two adjacent plates passing each other horizontally along a transform fault. It doesn't lead to the formation of any mountains but leads to seismic activity like earthquakes.
For example - the San Andreas fault in California, USA

Share:







Comments
Waiting for your comments