Atmosphere – Air Masses, Fronts, Cyclones, Anticyclones
by Devender
0 1637
Air masses, Fronts, Cyclones, Anticyclones are all parts of the atmosphere surrounding us.
Atmosphere – Air Masses, Fronts, Cyclones, Anticyclones
- Air Masses:
- Fronts:
- Warm Front:
- Cold Front:
- Occluded Front:
- Cyclones:
- Temperate Cyclones:
- Tropical Cyclones:
- Large sea surface with temperature exceeding 27 Degree C
- Coriolis force presence
- Vertical wind speed variation
- Upper divergence above sea level
- Tropical Cyclone's various names worldwide:
- It is known as a cyclone in the Indian Ocean, Arabian Sea & Bay of Bengal.
- It is called Hurricane in Atlantic sea (West indies) & USA
- It is called Typhoons in China and Japan sea
- In Western Australia, it is known as Willy Willies
- Anticyclones:
When air remains over a homogeneous area for a long time, it acquires characteristics of that area. The area can be vast plains or oceans where very little and only horizontal variations occur in temperature and moisture. These regions where air masses forms are known as source regions.
A front is the boundary zone that creates when two different types of air masses meet. The process is known as frontogenesis.
When a warmer and lighter air mass moves against cold and denser air mass, the warmer one rises over which is known as the warm front.
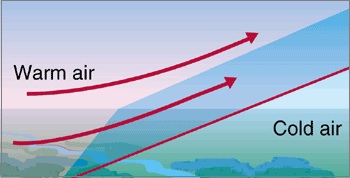
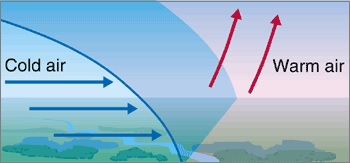
When a colder air mass forces its way under the warmer air mass by pushing it upward, the cold front is formed.
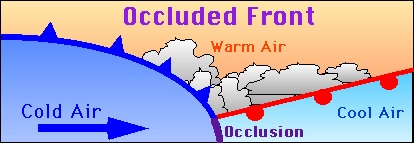
When a cold front lifts off a warmer front from the earth's surface, it is known as Occluded Front. After occlusion, the air masses lose their earlier characteristics and form new fronts and this meeting in the temperate zone gives birth to temperate cyclones along with both masses.
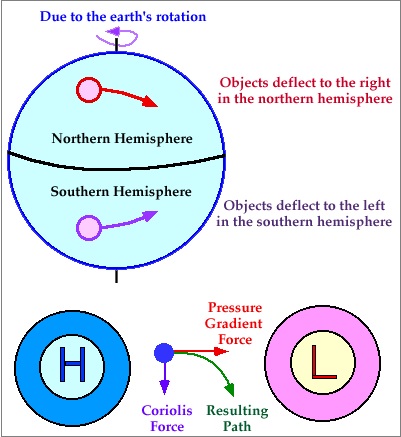
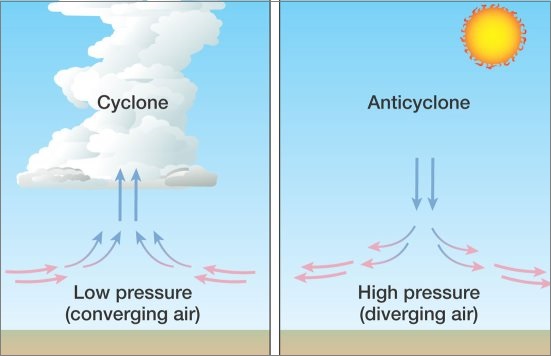
It is a low-pressure area surrounded by high-pressure areas from all the sides and the winds moving from all sides to central low. Under the effect of westerlies due to the Coriolis effect, the cyclones move in an Anti-clockwise direction in Northern Hemisphere and in a Clockwise direction in Southern Hemisphere.
However, there are no cyclones at the equator because the Coriolis force is not present there.
They are also known as wave cyclones or Extra-Tropical and mainly originate in zones b/w 35 – 65 Degree N & S of latitudes.
Cold air mass forces the warm mass upwards and a void is formed due to a decrease in pressure. The surrounding air tries to fill this void and hence, a temperate cyclone is formed. The average speed of this cyclone is 32 km/hr in summer and 49 km/hr in winters.
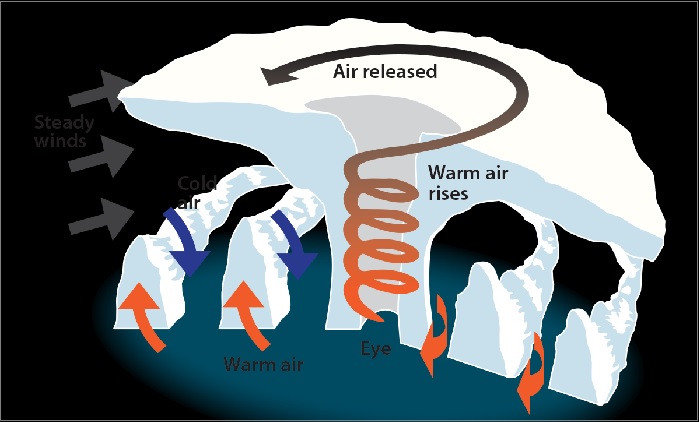
These are also known as Typhoons or Hurricanes and mainly originate in zones b/w 5 – 30 Degree N & S of latitudes. These are very violent in nature, originate over oceans in tropical areas & move to coastal areas. The violent winds, heavy rainfall & storm surges bring a lot of destruction.
The favorable conditions for the formation of tropical cyclones are:
The energy that intensifies the storm comes from the condensation process in towering cumulonimbus clouds that surrounds the center of the storm. So, the constant supply of moisture intensifies the storm.
However, when the storm reaches land, it dissipates because the moisture supply gets cut off.
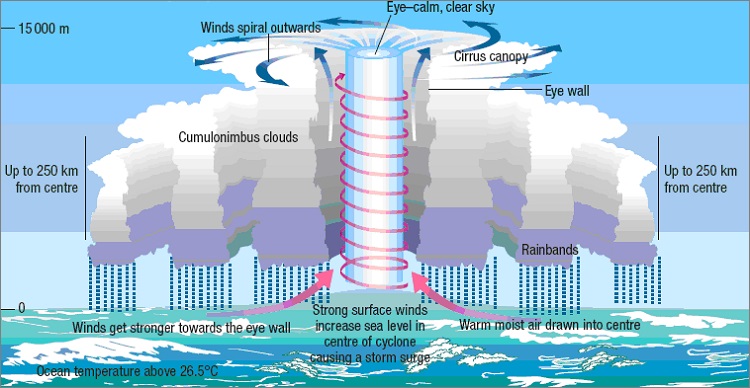
The place where a tropical cyclone crosses the land is called the landfall of the cyclone and the central low pressure is known as the eye of the cyclone. These are calm as the subsiding air has the lowest pressure and highest temperature.
Strong winds with clouds extending vertically surround this area. The eyewall surrounds the eye which is a place of strong spirally ascending winds to a height reaching tropopause, having max. wind velocity.
As the name suggests, an anticyclone is just the opposite of a cyclone. It is basically a large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure.
It goes clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and anti-clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere. The anticyclones are formed from air masses that cool more than their surroundings making the air contract slightly and hence, denser.
As the weight of the dense air is more, so the weight of the atmosphere in that area increases which increases surface air pressure. It provides fair weather, clearing skies, calm air with a high temperature in summers whereas cold in winters. Fog can also be noticed in regions of higher pressures.

Share:







Comments
Waiting for your comments