French Revolution and Napoleonic Wars
by Devender
0 2525
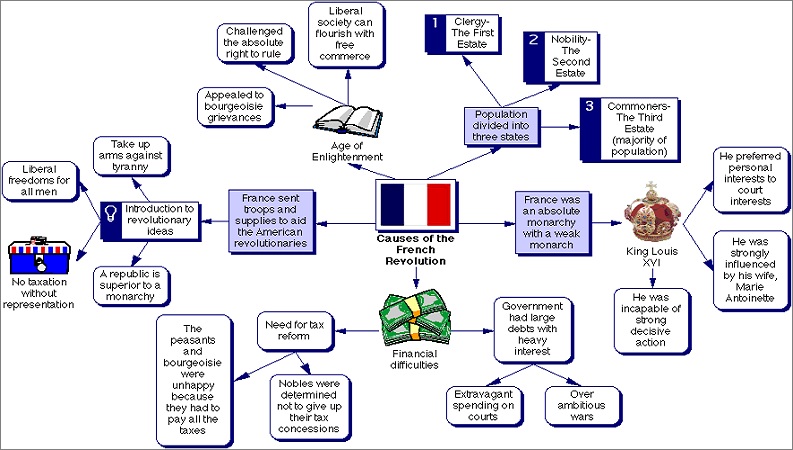
Society of eighteenth century France was partitioned into three classes or estates. The Clergy was the primary home, the Aristocrats were the subsequent home and the third estate, which framed most of populace, incorporated the working classes, the craftsmen, the city labourers and the workers (80% of the populace).
Clergy was the biggest landowner in per capita terms. Nobility had an imposing business model on every one of the significant authority positions in the taxpayer driven organization, the military, and other public workplaces.
The Third Estate didn't have voting rights. Then again, the Clergy and the Aristocrats didn't pay any tax and the taxation rate was exclusively borne by the Third Domain. This was a significant hotspot for the complaint of individuals.
Causes of French Revolution
- Unpopular Monarchy & financial troubles:
- Role of Enlightenment Thinkers
- Renaissance of 14th century
- Reformation of 16th century
- The Scientific Revolution
Lord Louis XVI was a wasteful ruler and under him France was in monetary difficulty because of expensive conflicts like the Long term War. The American Revolution had pushed France to bankruptcy as France had helped the Americans against England. While France upheld the American Revolution, the manner in which the Government administered in France was an enemy of proposition to the thoughts that framed the establishment of the American Revolution.
Enlightenment thinkers grounded their contentions on Realism, joy of Man, Majority rule government, Freedom and Secularism. The Precept of Nature brought the Church enduring an onslaught by the masterminds. Voltaire accepted that all religion was ridiculous as it was against the rationales of reason.
Agnostics and Realists acquired prevalence as it was underscored that man's predetermination lay in his own hands. The standards of Free enterprise and No Imposing taxes without any political benefit were focused on which brought the Honourability under analysis.
Events in French Revolution
In 1789, King Louis XVI assembled a conference of Home's General to get assent for extra assets. Third estate delegates went against extra financing since they were the ones who were the lone citizens and would need to bear the taxation rate from any such extra subsidizing.
In spite of the fact that they had requested and gotten twofold portrayal for the Get together, they were irritated when they came to realize that every one of the 3 estates were to have equivalent votes regardless of the quantity of agents. At the point when the discussions arrived at an impasse, Third Domain delegates proclaimed themselves the Public Gathering, a get together individuals instead of a gathering of the estates.
Before long they moved their gathering to the close by Imperial Tennis Court. Their objective was to draw up a constitution for France in which the Third estate could likewise have casting a voting rights. The Subsequent Home considered this to be an endeavour to get rid of the Old Request, and constrained the Ruler to squash the Public Get together.
At the point when the Ruler sent in troops to disperse the heads of third estate, individuals got incensed and they proceeded to tear open the Bastille Jail. They liberated the detainees and assumed responsibility for the arms and ammo put away in the jail. This was an emblematic rebel against the Lord and denoted the true finish to his position.
After Bastille occasion, the Public Get together begun enacting and it received the now well known record of French Insurgency, called the Privileges of Man and Resident. They annulled Feudalism, eliminated the Roman control on the French Church and shortened the forces of the Congregation to diminish their impact in commonwealth. The French progressive conflicts were battled from 1792 to 1802, by France, against the outright governments of Austria, Prussia and Savoy (Italian State) as the last wanted to shield their own hang on power from being dissolved by thoughts of freedom and uniformity.
They are known as Revolutionary wars since France was attempting to protect the revolution of 1789, which was under danger from adjoining governments which feared the French insurgency spreading to their nations. Consequently they needed to restore Government in France.
The French powers attempted to enrol the help of individuals of the region they oversaw, by offering them help and the thoughts of club, freedom and equity. In 1793, the Lord and the Sovereign of France were executed and afterward France pronounced a pre-emptive conflict against England, Holland, Spain and Hungary.
Jacobins & Napoleon
To qualify as elector, an individual needed to have pay over a specific edge. Because of this contingent Option to Cast a ballot, larger part of the Third Bequest could in any case not become electors. The Privileged was currently supplanted by the Average and the states of the labourers and city labourers didn't improve as they had anticipated. Before long, in 1793, the extreme Jacobins came to control in France. They made the Option to Cast a ballot unqualified by eliminating the income clause.
Robespierre, the head of the Jacobins was the man behind, what came to be known as, the Rule of Dread, where the system looked to execute through guillotine every one of the individuals who went against the insurgency. Lord and the Sovereign were executed in 1793. Before long the guillotine was utilized to rebuff anybody voicing question. Under the Jacobins, France slid into insurgency with little extension for Law and order.
Before long the actual Jacobins betrayed Robespierre and the Rule of Dread reached a conclusion with his execution by means of guillotine. Average again came to control and their administration was called Directorate.
In 1795 they reworked the constitution re-establishing the contingent Option to Cast a ballot. In 1799, Napoleon, in an overthrow, brought France under military principle. He proclaimed himself the Sovereign a couple of years after the fact and the Government was re-established in France.
The years somewhere in the range of 1803 and 1815 are known for Napoleonic conflicts, wherein the French battled against rest of Europe and carried the thoughts of French Unrest to the vanquished regions. Napoleon's powers nullified serfdom and modernized the organization of the vanquished regions in Europe.
After Napoleon's loss at Waterloo (Joined Realm of Netherlands-present day Belgium), the governments in rest of the Europe assisted the old tradition with coming to control in 1815. However, the government would never re-establish its control to the level saw before the 1789 upset and soon France saw four floods of insurgencies to at last turn into a Republic in 1871.
Impact/Constructive Criticism of French Revolution
The wars with France weakened the European colonial powers like Spain and Portugal and their colonies in South and Central America declared themselves as independent republics. Simon Bolivar from 1813 to 1824 liberated many South American countries and later tried to organize them into a US type federation in form of Gran Columbia. He freed Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Bolivia from the Spanish rule through an armed revolt.
The abolition of Slavery after French revolution was the first move against this repressive system and Britain followed suit in 1833 while USA banned it in 1865. It led to destruction of feudalism in France as all laws of old feudal regime were repealed and lands of the nobles and church were confiscated and redistributed. The privileged classes i.e. first and second estate, were abolished.
Anti-Feudalism wave that hit Europe in 19th century owes its origin to the events in France. French revolution ushered in the new economic system of Capitalism as against the prevalent Feudalism.
Jacobin constitution, which although never came into effect, was the first genuinely democratic constitution. It gave the right to vote to all, and even the Right to Insurrection, which implies the right to revolt or rise against the government. The Government under the Jacobin constitution had the responsibility to give work to all and "Happiness" of people was to be overarching state policy.
Under Napoleon’s rule, Napoleonic Code as a civil code for France, was introduced and some of its provision like merit based recruitment to government jobs and focus on clearly written law, continue to effect the present legal system in France and other nations.
French Revolution inspired movements against colonialism in colonies around the world, while movements for democracy and self-rule rose in whole of Europe.
- Negative impact of French Revolution
French Revolution had restricted achievement in accomplishing its destinations. Actually, present insurgency system fizzled on resolve the complaints of the workers who were the principle power during the uprising of 1789; just the peasants profited (as they became proprietors of land seized from the advantaged classes).
The revolution failed to bring in democratic rule and the Rule of Fear under the Jacobins was a mass butcher described by only savage power and penetrate of law and order.
Napoleon, because of his consistent fighting brought about ascent of patriotism in the attacked regions and he came to be seen, not as a saviour, but rather a conqueror.
This Patriotism was to demonstrate worthwhile to the unification of Germany and Italy in 1870s.

Share:







Comments
Waiting for your comments