Colonialism in Pacific, Central Asia and China
by Devender
0 1897
Monroe Doctrine was introduced by USA in 1823. It put focus on two things:
- Policy of Isolation
- Control of US in North and South America.
Doctrine basically said that USA will not interfere in the European affairs nor will tolerate any interference in its affairs.
Colonialism in Pacific
USA emerged as a new superpower by 1890s. It started to acquire new territories outside America under its control and extended it to Pacific and China.
Cuba and Puerto Rico were the only Spanish colony in America due to which Spanish-US war occurred in 1898. Philippines came under attack by USA and it came under control of USA. Spain gave away the control of Puerto Rico and Guam to the USA. Although, Cuba was officially made independent but still its foreign policy was controlled by USA. USA didn't allow Cuba to make any treaties with any other nation than USA.
- In 1898, USA officially acquired Hawaii
- In 1899, USA and Germany divided Samoan islands
Colonialism in Central and West Asia
Russia and Britain were the main rivals to acquire colonies in the Central and West Asia. Russia wanted to control the ports to access the sea for trade. Russia lost the Crimean war against the alliance of France, Britain, Ottoman Empire and Italy after which Russia started expanding in Asia.
In 1858, Russia constrained China to give up a tremendous area north of the River Amur building up a large part of the modern border between Russian Far East and Manchuria (China). This provided Russia a port in Western Pacific. To check Russian impact in Tibet, Britain sent soldiers there in 1904 and procured command over Tibet's international policy.
Russia became weak after the defeat in Russo-Japanese war, So it made a treaty with Britain and recognised Tibet and Afghanistan as areas of British control.
Subsequently, British had the option to make a support zone between India and Russia. In Persia (Iran), according to the 1907 understanding, Northern Iran was perceived as range of prominence of Russia, Southern Iran of Britain and the Central Iran was made a cradle zone with equivalent opportunity for both.
The vast majority of the Far East was mixed by 1871. Russia had 33% of the space under its influence. In the East Asia, China and Japan were free. Japan got away from Imperialism and set out on Industrialization after 1868 Meiji Restoration. It got colonialist in 1890s and accordingly it was China, which turned into the objective of Imperialism in nineteenth and twentieth century.
Colonialism in China
By 1730 all European countries were exchanging with China, while USA began exchanging 1784. China followed a strategy of separation after Europeans began intruding in internal matters, particularly the Christian Missionaries from Rome. China permitted just restricted exchange through chosen Chinese dealers and just by means of port of Canton.
- Two Opium wars:
In nineteenth century, Britain had become a significant exchange accomplice yet it had a colossal import/export imbalance as China was independent and imported little from the West. English were confronting the weight of this import/export imbalance as the Chinese acknowledged just valuable metals like Gold as instalment for fares to Britain (particularly Tea and Silk).
As an answer for this issue, the British began pirating Opium in China and began paying from the benefit gathered from carrying. This was opposed by China and brought about Opium Wars in 1840-42 and 1858.
After the principal Opium war -
A French missionary was murdered in China. This brought another war where France and Britain fought against China which resulted in the Treaty of Tianjin. The main focuses of treaty were:
After the second Opium war, China was open to foreign nations and hence, many European nations, some South American nations and Japan made trade relations with China. China became open for imperialism under several powers.
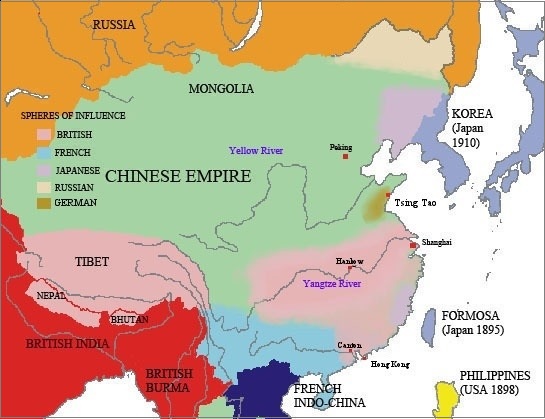
China became very weak after the second opium war and when Russia threatened to attack, it was forced to hand over a large territory north of River Amur to Russia.
This war was fought between Japan and China between 1894 and 1895. This conflict was battled basically over Korea, which was heavily influenced by China.
After the misfortune, China perceived Korea as an Independent state. However, Japan occupies Korea in 1910. China had to pay about $150 million to Japan as a compensation for damages of War.
The result of this war was:
China had to pay compensation to Japan but it had no funds so it reached to Britain, Russia, France and Germany for loans. They provided loans to China but in exchange, they divided China in to sphere of influence. It meant these countries had parts of China where they had exclusive rights to do anything. It was called as "cutting of the Chinese melon".
In 19th century, China was divided in to sphere of influence and it seemed to be partitioned soon in to different parts where each power had its own territory. A rebellion known as Boxer rebellion was started in 1899-1900 against the interference of foreign nations in China's politics, economic and religious affairs but soon it was crushed by joint forces of all these nations.
China was forced to pay huge amounts as compensation for damages to foreign property in China. A protocol was signed known as Boxer protocol which enabled these nations to station their troops in China for protection of their citizens. Russia continued to occupy Manchuria.

Share:







Comments
Waiting for your comments